Target-date funds are a great way for investors to gain exposure to investments that match the risk tolerance best suited to their current stage of life. The funds allow investors to:
- Accumulate wealth via higher-risk/higher-return retirement assets early in their careers
- transition toward preserving wealth by holding an increasing higher allocation of less-risky, fixed-income investments as time progresses
Vanguard, Fidelity, Schwab, T. Rowe Price and a number of other fund providers offer these products through various tax-advantaged investment plans and after-tax brokerage accounts.
Any investment entails risk. Markets go up, markets go down. When that happens, your balance in the investment will naturally change. That’s market risk, and it’s just one type of risk you’re exposed to when you invest. There’s also interest rate risk, inflation risk, currency risk, and many more.
However, target-date funds attempt to lessen the severity of some risk by gradually and automatically transitioning your asset mix of stocks and bonds to a more conservative mix as you approach retirement. This is obviously a time you’ll need the money you’ve saved during your wealth accumulation phase and transitioned toward wealth preservation. Both are crucial components for reaching financial independence.
Because no two are the same (no cookie-cutting here), let’s learn more about these powerful products used by millions to prepare for a safe and secure retirement.
Disclaimer: This article does not constitute individualized investment advice. Securities, funds, and/or other investments appear for your consideration and not as personalized investment recommendations. Act at your own discretion.
Table of Contents
What Are Target-Date Funds?

Target-date funds invest in assets that match the recommended risk preferences of investors with their intended retirement date. Depending on the age at purchase, the mix of underlying assets comprises various allocations toward stocks and bonds.
While all funds aren’t the same, most follow a similar strategy:
- Pick the fund closest to your intended retirement date.
- Invest money across time.
- Have a fund manager adjust the mix of stock, debt, and cash to become more conservative over time.
However, despite these simple steps, these funds can differ dramatically. This includes the investments held in each fund, various levels of fees associated with the fund and underlying investments, and even what happens with the investments from present to target date and beyond (“to” vs. “through”).
In fact, some funds cease the transition to more conservative investments at the target date while others transition slower and continue shifting toward more fixed-income/cash allocations. The advantage of the latter would be more potential for growth into your retirement years.
For target-date funds to qualify as one of the best investments for young adults, I’d only consider the latter (“through” retirement) since continued portfolio growth in our later years is important. I say this because as things currently stand, we might not have as many retirement resources as our parents and grandparents with Social Security and Medicare currently slated to run out of money before we retire.
And let’s face it, despite reaching your goal, you might still need more capital appreciation going forward. If you consider the amount of time you’re likely to spend in retirement, which could be 30 years or more, it becomes clear a need still exists for capital growth from stocks and also some combination of income-generating assets.
How Do Target-Date Funds Work?
Target-date funds offer the simplicity of investing in one product and having the asset allocation change over time as you age. This allows for a transition from more stocks to more fixed-income and cash-equivalent investments to match your recommended risk levels by age.
This transition, referred to as the “glide path,” can help investors who do not pay close attention to their retirement holdings across time. An investor need only select the fund best-matched to their intended retirement date and hold the investment. This results in better tax consequences (discussed below) and eases concern by not needing to worry about rebalancing, asset selection, or any other investing due diligence.
Are Target-Date Funds a Good Investment?

According to a CNBC article, one man who held employer-sponsored retirement accounts from four previous employers and one from his most recent employer, saw his losses would have been significantly less had all the assets been invested in an equivalent target fund in his most-recent employer’s retirement fund. His previous employers’ retirement accounts heavily invested in stock portfolios and resulted in far steeper losses than he would have under a comparable stock/bond allocation in his target fund.
Target-date funds would have transitioned some of his funds from stocks to bonds and possibly resulted in smaller losses.
Looking at Morningstar’s data included in the article, we can see accounts held in funds closer to retirement performed less-poorly than those intended for later dates. This is because those later-dated target funds held higher allocations in equities and thus experienced more adverse returns during the recession.
For investors who wish to automate their retirement savings in diversified, low-cost passive investments, target funds can be valuable financial instruments. The funds automatically transition from heavier stock allocations to bond allocations as the employee ages, thereby taking less risk in their retirement portfolios.
If these types of investments interest you, consider opening an account with J.P. Morgan Self-Directed Investing. The service boasts over 10,000 mutual fund options and allows you to invest in a large number of target-date funds.
Investing through a free stock app like J.P. Morgan Self-Directed Investing also offers you the opportunity to invest in individual stocks, ETFs, options and more. Consider opening an account today.
- J.P. Morgan Self-Directed Investing delivers unlimited commission-free online stock, ETF, mutual fund, fixed-income, and options trades.
- Choose an account that's right for you: General Investing, Traditional IRA or Roth IRA.
- Access your account through the secure, easy-to-use trading experience online or through the Chase Mobile® app.
- Use J.P. Morgan's powerful tools and resources to help you take control of your investment.
- Special offer: Open an account today and earn a cash bonus of between $50 and $700 when you open and fund an account with qualifying new money.*
- Better-than-average commission-free asset selection (includes mutual funds and Treasury bonds)
- Multiple investment account types
- Integration with other Chase banking accounts
- Extremely smooth and intuitive mobile experience
- Limited research and other investing tools
- Must have at least $2,500 in your account to use Portfolio Builder tool
Related: Best Investment Apps for Beginners to Start Investing
Are Target-Date Funds Held ‘To’ or ‘Through’ Retirement?
Target-date funds continue holding equities in a person’s portfolio when entering retirement. However, the allocation will depend on whether the investor has access to target-date funds which transition “through” retirement or “to” retirement. The former offers a greater allocation in equities because these funds understand the holder continues to seek capital appreciation through a higher stock allocation than fixed income investments. The latter holds a more conservative allocation.
More specifically, target funds inherently manage an investor’s assets in relation to an intended retirement date. With target-date funds employing the “to” approach, this results in funds adopting higher allocations to fixed income investments at or toward the retirement date. The investor’s portfolio allocation will remain static thereafter.
Whereas with “through” retirement target-date funds, the retirement date helps guide investors through retirement with the goal of accumulating wealth long after the retirement date. Funds which adopt this approach have higher stock allocations at the target date and follow with a decreasing allocation 10-30 years post retirement. These fund approaches differ dramatically in terms of risk/return potential. Make sure you understand the risk/reward trade-off made through these funds and how they invest in stocks and bonds over time.
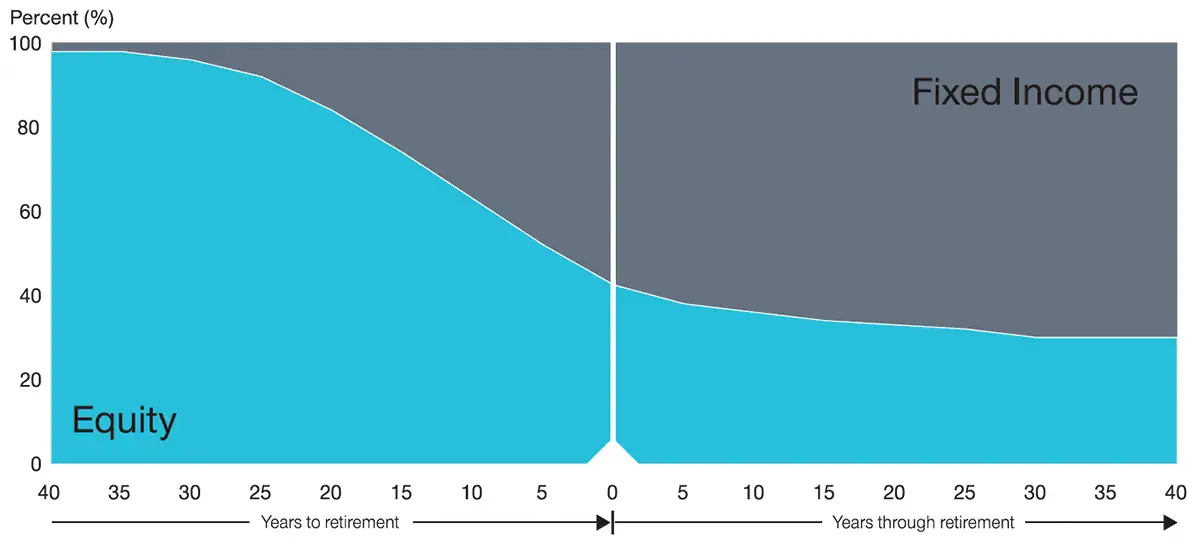
The charts below illustrate the differences in allocations to stocks and bonds in both a “to” and “through” approach. As you can see, both graphs show changes in allocations over a 50-year-plus period.
The “to” approach emphasizes the static glide path (consistent slope of the change in allocation over time) while the “through” approach emphasizes a steepening decline in its glide path beyond retirement.
Target-Date Fund Held Through Retirement
Target-Date Fund Held To Retirement
Track Your Net Worth with Either Fund Type
Regardless of the fund type you have, “to” or “through,” you will want to track your net worth over time to ensure you remain on track to meet your overall investing objectives.
The best free resource I’ve found for tracking your net worth is Empower.
Empower is one of our top-rated financial services firms for people of any income level thanks to its suite of free-to-use tools.
The free Personal Dashboard makes it easy for people to add all their financial accounts (including credit cards, savings, checking, loans, and tax-advantaged investment accounts) in one place.
Empower offers a number of investing and personal finance tools that you’d expect from a free service, such as the Savings Planner, Retirement Planner, and Financial Calculators—all intuitive and well-built.
But where I think Empower really shines is its free Investment Checkup tool. The tool assesses your portfolio risk, analyzes past performance, and even provides a target allocation for your portfolio. Many people don’t realize how much of their varying mutual funds and ETFs overlap with one another—but the tool can actually help you identify overweight and underweight sector investments (maybe you have too many assets in utilities and not enough in health care) and assess your true diversification.
You can even compare your portfolio to both the S&P 500 and Empower’s “Smart Weighting” Recommendation, which suggests that investors more equally weight their portfolios across size, style, and sector—unlike the S&P 500, where the biggest stocks have the most effect on the portfolio, and there are huge differences in how much each sector is weighted.
Use our exclusive link to sign up for the Empower Personal Dashboard. If you have $100,000 or more in investible assets, you’ll also be able to schedule a free initial 30-minute financial consultation with an Empower professional.
- Empower offers both a free set of portfolio, net worth, and cash flow tracking tools, as well as paid asset management service.
- Link Empower to your bank and investing accounts, credit cards, and more to see a single view of useful information and data, including your net worth.
- Empower Advisory Group offers a comprehensive wealth management service known as Personal Strategy. This managed account solution provides clients with discretionary investment management, personalized portfolio construction, and access to financial planning support. Accounts investing $100k to $250k receive unlimited advice and retirement planning help from financial advisors, as well as a professionally managed ETF portfolio with reviews upon request. Higher asset tiers offer access to dedicated advisors, estate planning, and tax specialists, plus additional investment options like access to private equity.**
- Special offer: If you have $100k+ in investible assets, sign up with our link to schedule a free initial 30-minute financial consultation with an Empower professional.
- Free portfolio tracker (Dashboard)
- Free net worth, cash flow, and investment reporting tools (Dashboard)
- Tax-loss harvesting (Personal Strategy)
- Dividend reinvestment (Personal Strategy)
- Automatic rebalancing (Personal Strategy)
- Low investment expense ratios (Personal Strategy)
- High number of investment accounts supported (Personal Strategy)
- High $100k minimum for investment management (Personal Strategy)
- Moderately high investment management fee (0.89% AUM) compared to other online advisors (Personal Strategy)
Related: Best Portfolio Analysis Tools [Portfolio Analyzer Options]
What Are the Best Target-Date Funds?

Low-cost target-date funds can be great for holding an entire retirement account’s portfolio. That’s because the underlying assets will typically be low-cost actively managed or index funds that provide both diversification, as well as risk management (through the glide path feature).
But I’ll emphasize low cost. If the fees for a target-date fund exceed 1%, and you could DIY your own portfolio with much lower fund fees in either your workplace account or your own retirement account, it might make sense to take management into your own hands. Just know that doing so requires manually adjusting your allocation between stock and bond mutual funds/holdings across time. This also runs into complications with behavioral finance concerns.
Or, of course, you could just find a lower-cost target-date fund from one of the families below.
Make Young and the Invested your preferred news source on Google
Simply go to your preferences page and select the ✓ box for Young and the Invested. Once you’ve made this update, you’ll see Young and the Invested show up more often in Google’s “Top Stories” feed, as well as in a dedicated “From Your Sources” section on Google’s search results page.
Vanguard Target-Date Funds

Choosing the best target-date fund depends on the number of years to retirement but you will want to choose funds with lower costs.
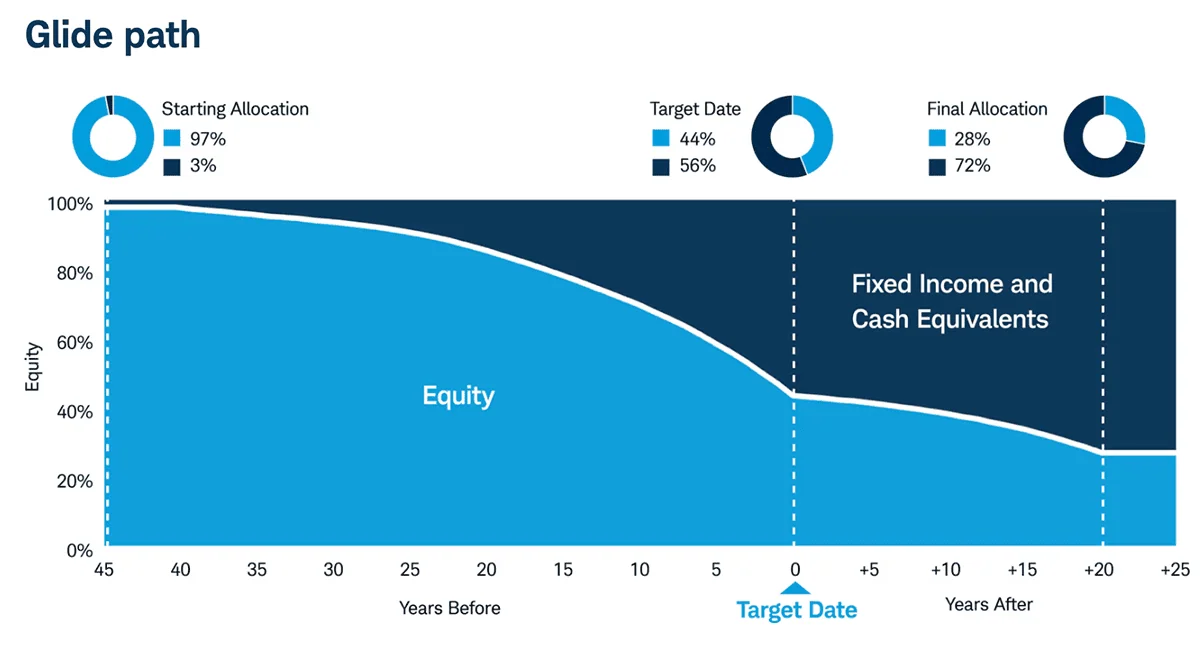
I’ll start with Vanguard’s target-date fund series. Vanguard Target Retirement Funds are a dirt-cheap option, charging just 0.08% annually (or 80¢ on every $1,000 invested) across the entire lineup (as of December 2024); per Vanguard research, the industry average expense ratio for comparable target-date funds runs 0.48%. The series currently is composed of 12 funds—11 dated funds (2020, 2025, and so on), as well as the Vanguard Target Retirement Income Fund (VTINX), designed for people already in retirement who want to generate income with a little potential for capital appreciation.
Vanguard offers a number of target-date index funds, but the ones of most interest to this site’s readers (young adults) are likely the Vanguard Target Retirement 2060, 2065, and 2070 Funds (VTTSX, VLXVX and VSVNX, respectively).
Vanguard keeps its expense ratios low by investing in a handful of passive index mutual funds. The only active management here is happening at the fund-allocation level; that is, how much of each bond or stock fund that each target-date fund decides to hold.
A look at the glidepath for Vanguard Target Retirement Funds:
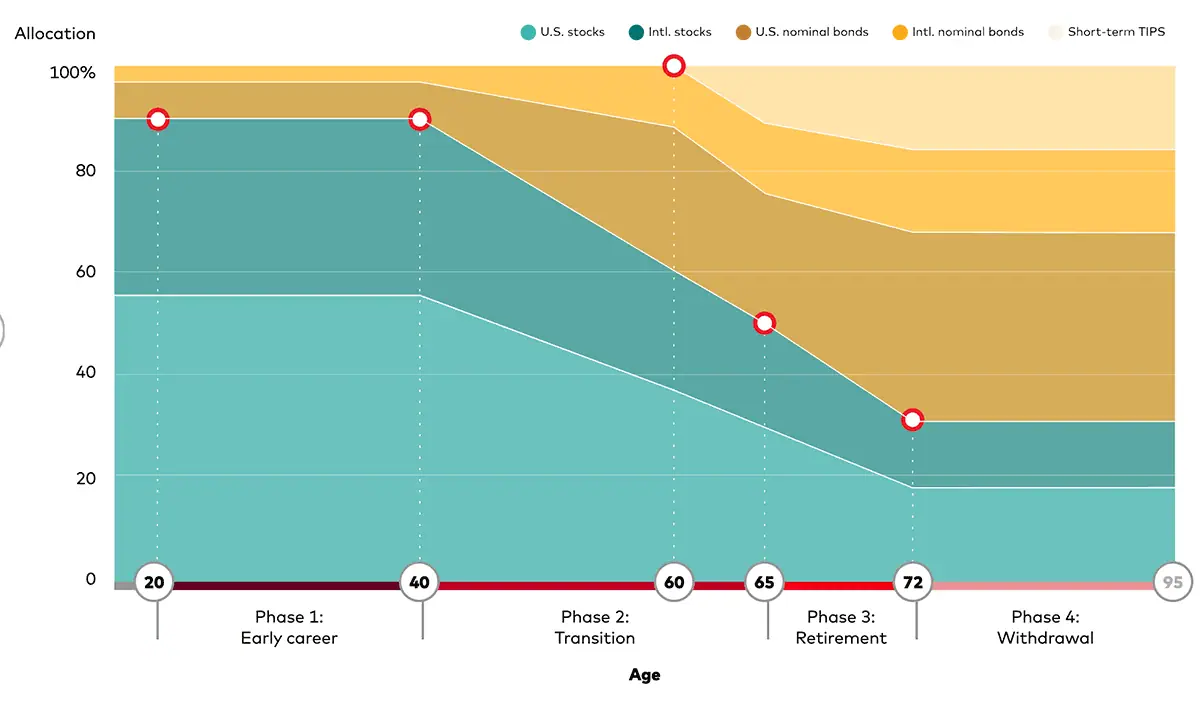
You can learn more in our primer on Vanguard target-date funds.
Fidelity Target-Date Funds

You actually have four lineups to choose from if you want a Fidelity target-date fund:
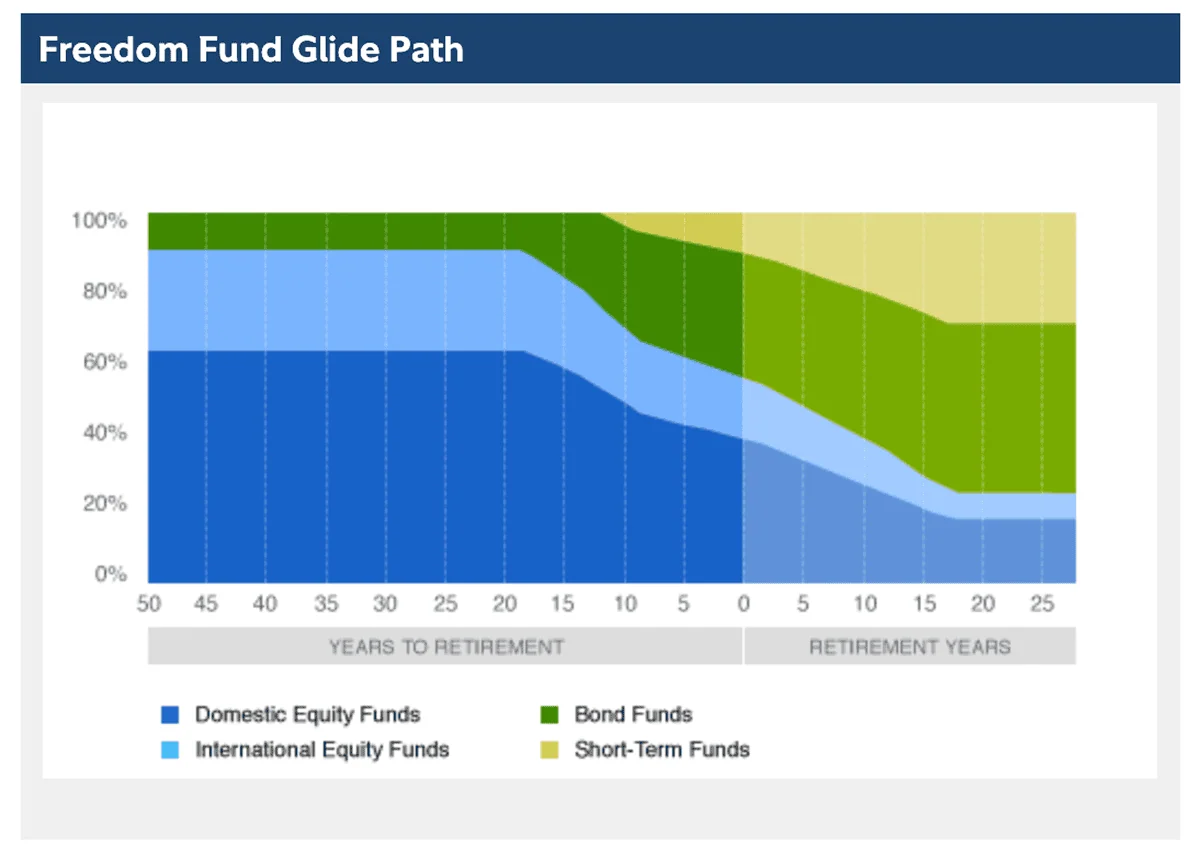
Fidelity Freedom Funds are a family of 14 target-date funds whose dates run from 2010 to 2027, plus the income-focused Fidelity Freedom Retirement Fund (FFFAX). These target-date funds predominantly (but not entirely) hold actively managed funds. That elevates costs a bit; they currently run between 0.46% and 0.68% annually.
Fidelity Freedom Index Funds, which run at just 0.12% annually, are built exclusively from Fidelity’s lineup of low-cost index funds.
Fidelity Freedom Blend Funds earn their name from holding a “blend” of actively managed and indexed funds. The result? Expenses that fall between the two prior lineups, ranging from 0.41% to 0.47%.
This is what the glidepath for Fidelity Freedom funds looks like:
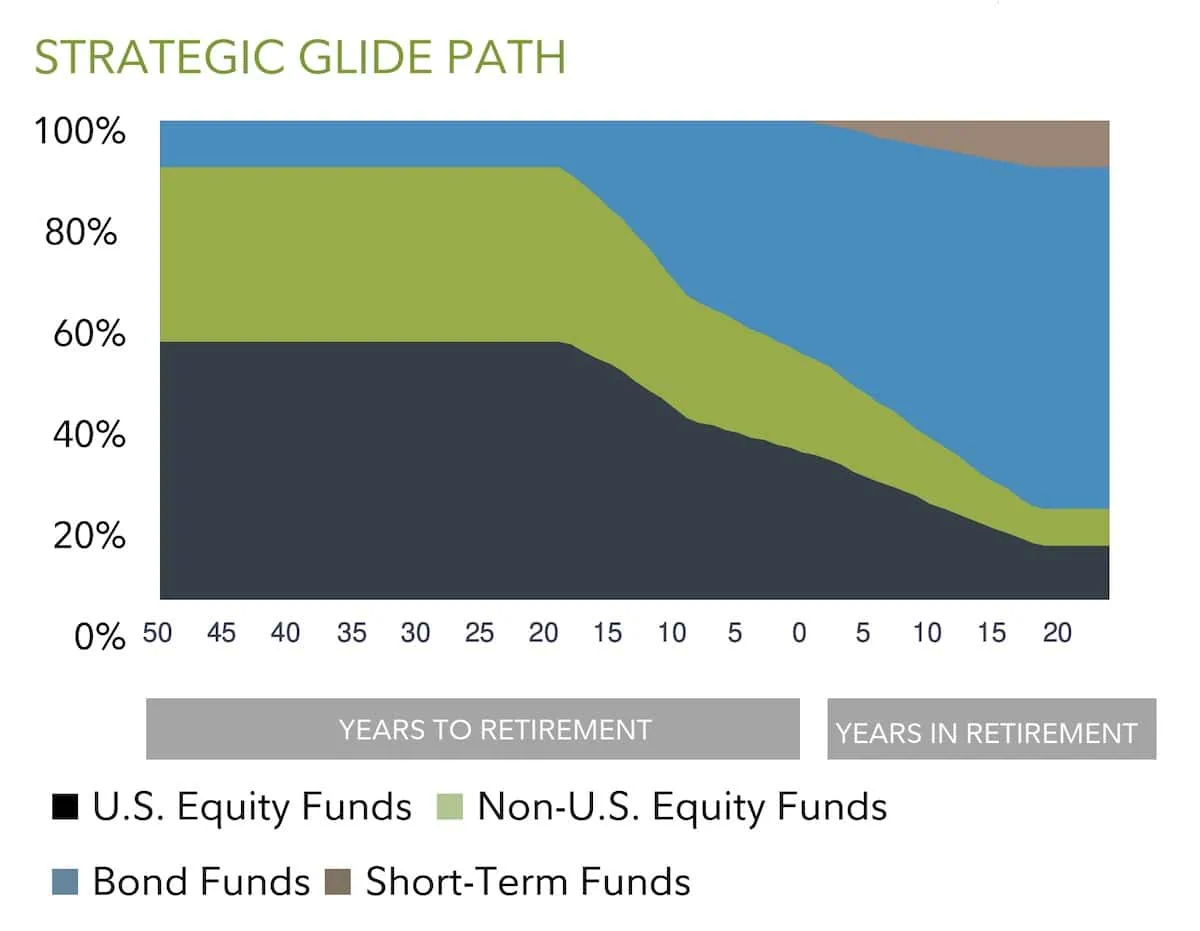
Fidelity Sustainable Target Date Funds are Fidelity’s newest target-date lineup. These funds, which range from 0.41% to 0.49% in annual expenses, invest in either actively managed funds that select securities based on ESG characteristics, index funds that track an ESG index, or funds that don’t necessarily have a principal ESG strategy, but that have at least 80% of assets in debt securities that the adviser believes have positive ESG characteristics.
Here’s a look at the Fidelity Sustainable lineup’s glide path:
You can learn more in our primer on Fidelity target-date funds.
T. Rowe Price Target-Date Funds

T. Rowe Price also has dozens of target-date funds, spread across three families:
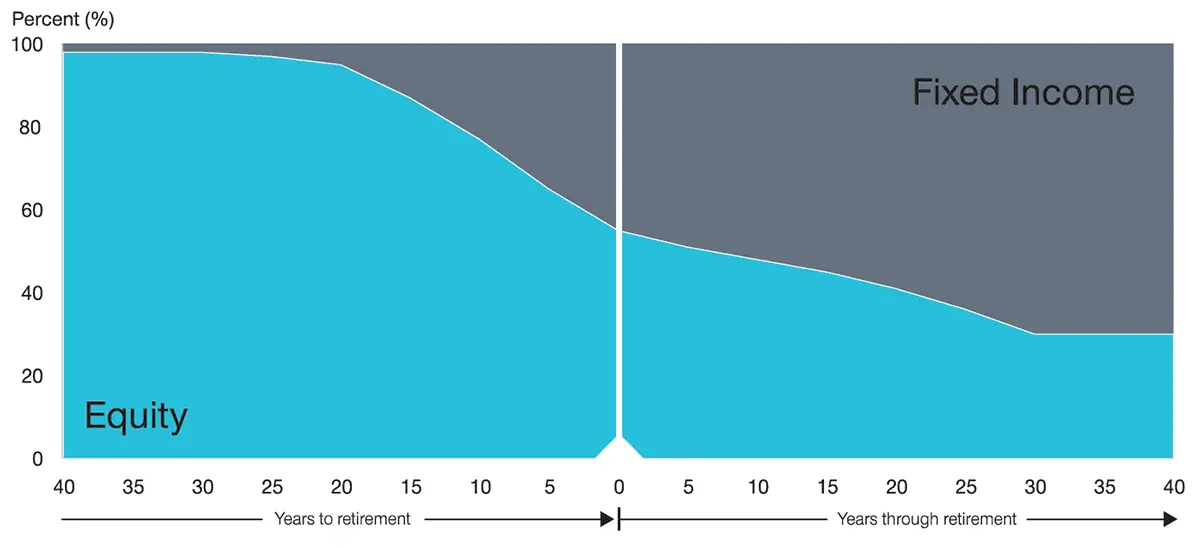
T. Rowe Price Retirement Funds include 14 dated funds, as well as two income funds. These funds are run by a management team that averages 19 years of experience, and hold various actively managed T. Rowe mutual funds to achieve their goals. Net annual expenses range from 0.49% to 0.64%.
T. Rowe Price Retirement Blend Funds, like with Fidelity’s blended lineup, strike a balance between indexed and actively managed holdings that helps cut down on cost. This line’s average expenses range from 0.34% to 0.44%.
Here’s a look at the glidepath for the Retirement line:
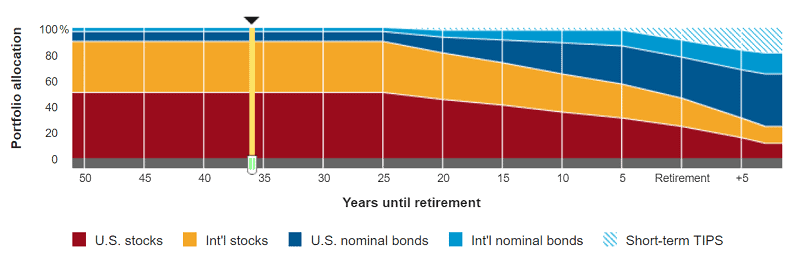
T. Rowe Price Target Funds, made up of 14 dated funds, are among the more interesting varieties across all the major fund providers. T. Rowe’s Target Funds provide higher exposure to bonds across the glide path. While it’s not a drastic difference, it provides more stability for less risk-averse investors. And as you can see from the graphic below, that greater emphasis on fixed income starts pretty early. Expenses here range from 0.45% to 0.64%.
T. Rowe Price Target Funds have a somewhat different glidepath:
My previous employer partnered with T. Rowe Price for our 401(k) plan and would default new employees into these target-date funds when retirement benefits began accruing. Many employees likely remained in these funds with their retirement contributions.
→ Schwab Target-Date Funds
Schwab also has a pair of target-date funds, one of which competes directly with Vanguard on price:
Schwab Target Funds range in five-year increments from 2010 to 2065, with new iterations added over time. Each target-date fund holds a mixture of stock mutual funds and fixed income mutual funds, with the percentage allocated to stocks gradually getting higher the further out the targeted retirement date is. Schwab Target Funds also are OK with holding both actively managed and index funds. Expenses range from 0.25% on the low end to 0.58% on the high end.
Schwab Target Index Funds, as the name would suggest, invests exclusively in index funds. However, unlike many other target-date fund families, this Schwab lineup gets its exposure from exchange-traded funds. For instance, Schwab Target 2025 Index Fund (SWYDX) has holdings in Schwab ETFs such as the Schwab US Aggregate Bond ETF (SCHX) and the Schwab US Large Cap ETF (SCHX). The result is a low 0.08% annual expense ratio across the board, on par with Vanguard Target Retirement Funds.
Here’s what the glidepath looks like for Schwab’s target-date lineups:
Schwab vs. T. Rowe Price vs. Fidelity vs. Vanguard Target-Date Funds

→ Expense Ratios
Over the long term, expenses matter a great deal. And given that annual expense ratios affect your long-term performance, you should consider them strongly when selecting a target-date fund.
To give you a flavor for how these companies’ expense ratios compare, have a look at the following tables. The first table focuses on traditional (actively managed) target-date funds, while the second focuses on indexed TDFs.
Expense Ratios - Schwab vs. T.Rowe Price vs. Fidelity vs. Vanguard Target Date Funds (NON-INDEX)
| Target Date | Schwab Target Series (non-Index) | T. Rowe Price Retirement Series (non-Index) | Fidelity Freedom Series (non-Index) | Vanguard (Only offers index TDFs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2030 | 0.40% | 0.55% | 0.61% | N/A |
| 2045 | 0.52% | 0.60% | 0.68% | N/A |
| 2060 | 0.58% | 0.64% | 0.68% | N/A |
| Data as of Oct. 6, 2025 | ||||
Expense Ratios - Schwab vs. T.Rowe Price vs. Fidelity vs. Vanguard Target Date Funds (INDEX)
| Target Date | Schwab Target Index Fund | T. Rowe Price Retirement Blend Fund Series (Doesn't offer true index TDFs) | Fidelity Freedom Index Series | Vanguard Target Retirement Fund Series |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2030 | 0.08% | 0.38% | 0.12% | 0.08% |
| 2045 | 0.08% | 0.41% | 0.12% | 0.08% |
| 2060 | 0.08% | 0.44% | 0.12% | 0.08% |
| Data as of Oct. 6, 2025 | ||||
→ Equity Percentage at Age 65 (Retirement)
Further adding diversity in these companies’ target-date funds lineups is the percentage of underlying assets held in equities at retirement age (65).
Given your investment objectives, you might wish to hold more or less equity in your portfolio at retirement, adding further complexity to your investment decision. Looking at these four companies, the following table shows the respective equity percentage held in the target-date fund families at retirement age:
| Target Date Family | Percentage of Equities @ 65 |
|---|---|
| Schwab | 44% |
| T. Rowe Price | 58% |
| Fidelity | 55% |
| Vanguard | 55% |
| Source: Schwab, T. Rowe Price, Fidelity, Vanguard | |
→ Asset Classes Represented
Another important consideration for choosing between these target-date funds is the underlying asset classes represented in each of the fund families.
Have a look at the following table to see the asset classes held in each target-date fund family.
| Asset Class | Schwab | T. Rowe Price | Fidelity | Vanguard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. Large Cap | X | X | X | X |
| U.S. Mid Cap | X | X | X | X |
| U.S. Small Cap | X | X | X | X |
| International Equity | X | X | X | X |
| Emerging Markets Equity | X | X | X | X |
| U.S. Fixed Income | X | X | X | X |
| U.S. TIPS | X | X | X | X |
| High Yield Bonds | X | X | X | X |
| International Bonds | X | X | X | X |
| Emerging Markets Debt | X | X | X | X |
| REITs | X | X | X | |
| Commodities | X | |||
| Source: Morningstar | ||||
Are Target-Date Funds Tax Efficient?

When investing in mutual funds and target-date funds, you purchase a security comprised of underlying assets (mutual funds or ETFs). When these underlying funds realize capital gains and/or dividends, these pass through annually to the shareholder, who pays the applicable tax.
For net capital gains (capital gains less capital losses), they come grouped into two buckets: long-term (securities held longer than one year) or short-term (held <1 year). The IRS taxes both at the appropriate rates for the shareholder, and depending, could result in paying no tax.
For dividends, fund managers accumulate and distribute these to shareholders throughout the year. Dividends receive ordinary income tax treatment unless they meet the requirements for qualified dividends. These distributions represent one form of taxation on target-date funds.
Investors can also transact by buying and selling the funds themselves, triggering another taxable event. Commonly, target-date funds are tax efficient in nature because they often require no transacting on your part to arrive at your asset allocation. As a result, the target-date investor faces fewer taxable events than an actively-managed portfolio.
However, because capital gains and dividends pass through to the investor regularly, if an investor holds these investments outside of a tax-advantaged account, this can trigger regular tax consequences. In other words, if the investor transacts less often with target-date funds (no worries about receiving a margin call from shorting stocks) than with active management, it can represent a more tax-efficient investment.
Are Target-Date Funds Actively Managed?

Target-date funds provide a simplified way to save for retirement. They offer exposure to a variety of asset classes, markets, and active and passive management (discussed below).
Regarding the active vs. passive management component, investors need to remain aware of the assets held in the target-date funds. Said differently, despite the simplicity of these investments, investors must should be conscious of the underlying asset allocation, fees, and portfolio risk of their target-date investments. In fact, some fund companies offer two type of target-date investments: target-date funds and target-date index funds.
Target-Date Funds vs Index Funds
Fund companies can offer two types of target-date funds:
- traditional target-date funds which hold a mix of passive and active underlying mutual funds meant to transition toward more conservative mutual funds as the investor ages
- target-date index funds which primarily invest in passive ETF investments from the fund company.
The former provides active fund management opportunities while the latter is primarily passive in nature. The active component results in higher expense ratios because this utilizes active managers who attempt to beat their relevant benchmark through stock picking or discretionary fixed-income selection.
Personally, I prefer the passive options for their cost and the removal of human emotion when it comes to decision-making. Having made some of my worst investing mistakes thinking I could beat the market, I opt for avoiding the uncompensated risk.
Regardless of choice, both types of funds offer diversification, asset allocation optimization, and rebalancing to keep on track if markets change.
Target-Date Funds Pros and Cons
Pros
→ Get a complete portfolio in a single fund. By electing one target-date fund, you have a straightforward approach to a sophisticated problem: how to invest successfully for retirement, whether in an individual retirement account (IRA), 401k, or other eligible retirement account. No matter the account type, be sure to take advantage of retirement plan limits.
→ Less risk through broader diversification. Each target-date fund available through Vanguard, Fidelity, T. Rowe Price, Schwab or other companies invests in index funds which track the broader market. Available options give you access to thousands of U.S. and international stocks and bonds, including exposure to the major market sectors and segments.
→ Professionally-managed asset mix. Each target-date fund has a manager who gradually shifts each fund’s asset allocation to a lower stock mix and more fixed income investments over time. This happens to make the investment portfolio more conservative the closer you get to retirement.
→ Automatic rebalancing. Because managers oversee these funds, they make sure to maintain the current target asset mix. This frees you from the hassle of worrying about ongoing rebalancing on a quarterly, semi-annual or annual basis. Essentially, the funds operate on a schedule laid out in the prospectus.
→ Low costs. Depending on your target-date fund company, your costs can fall on the lower side than managing the assets yourself. For example, Vanguard offers expense ratios 83% below the industry average. When you pay less for your target-date funds, this keeps more money for you and shows you just how to save money toward your retirement goals.
Cons
→ Tax inefficient. Depending on your investing strategy, target-date funds can represent tax inefficient investments. Capital gains and dividends pass through to the investor and can result in tax consequences if held outside of a tax-advantaged account. For this reason, target-date funds most commonly reside in tax-advantaged retirement plans.
→ Glide path variability. Depending on fund type, you might not hold the preferred allocation of stock, bonds, and cash. Some funds transition quicker or slower than your desired asset allocation. This can expose the investor to undue risk. Before purchasing a target-date fund, take a closer look at the allocation, glide path, and whether the fund employs a ‘to’ or ‘through’ retirement methodology.
→ Higher fees. Make no mistake about it, these higher-touch products come at a higher cost. Quite often, target-date funds can charge higher fees than mutual funds because they pass through not only the underlying mutual funds’ fees, but also their own management fees. Some target-date funds come with over 0.80% of annual fees based on the numbers shown above. These fees can compound and make it harder to learn how to build wealth.
Target-Date Funds Alternative

As an alternative, you can use a service like M1 Finance, which uses index funds and other stocks to replicate this same portfolio transition over time depending on stated financial goal.
Personally, my wife and I have looked into using M1 Finance for our IRA funds and setting a glide path which will transition our assets from primarily stock-based to fixed income as we age. If we choose to use target-date retirement funds, we will aim to use the “through” target-date fund methodology because my wife and I will want more exposure to equities in the long-term than fixed income. In the later years, we will want more money to transition to fixed income as we retire completely and have need for income as opposed to capital appreciation.
Conclusion
Personally, I am delighted to see many companies offer default investments into target-date funds. If an employee never logs into the account once after being hired, these investments are deemed more suitable than purely company stock or equity mutual funds. This is because the employee may have different risk preferences depending on where they are on their journey toward retirement.
For example, defaulting a 22-year old employee into an total market fund like VTI or VTSAX is suitable, whereas a new 60-year old employee likely would not make the same decision. When learning how to start investing money early in a career, these mistakes can be forgivable.
When retirement is just around the corner, this requires more suitable financial planning. Target-date funds remove this concern if employers default their employees into these funds. It is important to be mindful of the risks posed by markets, independent of the investments held in your account.
The only truly risk-free investments are insured savings accounts, certificates of deposit or Treasury bonds and notes. Being cognizant of the risks involved with investing is imperative. Target-date funds do a decent job of managing the risk better for employees as they age and near retirement.
Related: 17 Best Stock Research & Analysis Apps, Tools and Sites








![7 Best Value Stocks for 2026 [Smart Picks to Buy] 43 best value stocks for 2024](https://youngandtheinvested.com/wp-content/uploads/best-value-stocks-for-2024-600x403.webp)
![9 Best Non-Stock Investments [Alternatives to the Stock Market] 44 best non-stock investments](https://youngandtheinvested.com/wp-content/uploads/best-non-stock-investments.jpg.webp)
